# 字符串操作技巧
# 1、判断字符串是否包含某个字符
# indexOf
indexOf():查找某个字符,有则返回第一次匹配到的位置,否则返回-1
indexOf(要查的元素,开始查询的下标位置)
let str = "123456";
console.log(str.indexOf("1")); // 输出结果:0
console.log(str.indexOf("7")); // 输出结果:-1
console.log(str.indexOf("6",6)); // 输出结果:7
注:该方法同样适用于数组操作
# includes
includes():该方法用于判断字符串是否包含指定的子字符串。如果找到匹配的字符串则返回 true,否则返回 false
includes(要查的元素,开始查询的下标位置)
注:使用 includes()比较字符串和字符时是区分大小写。
let str = '123456';
str.includes('1') // 输出结果:true
str.includes('7') // 输出结果:false
str.includes('6', 6) // 输出结果:false
注:该方法同样适用于数组操作
# 2、字符串截取
# slice
slice() 方法用于提取字符串的某个部分,并以新的字符串返回被提取的部分,不改变原字符串。
slice(开始位置,结束位置)
结束位置不填写值时表示到字符串结尾处,负数则代表从结尾开始
let str = "abcdefg";
str.slice(1,6); // 输出结果:"bcdef"
str.slice(1); // 输出结果:"bcdefg"
str.slice(); // 输出结果:"abcdefg"
str.slice(-2); // 输出结果:"fg"
str.slice(6, 1); // 输出结果:""
注:该方法同样适用于数组操作,数组使用时是浅拷贝
# substring
substring() 用于提取字符串中介于两个指定下标之间的字符
str.substring(a, b)
a:需要截取的第一个字符的索引,该索引位置的字符作为返回的字符串的首字母。
b:(可选)一个 0 到字符串长度之间的整数,以该数字为索引的字符不包含在截取的字符串内。
substring 提取从 a 到 b(不包括)之间的字符。特别地:
如果 a 等于 b,substring 返回一个空字符串。
如果省略 b,substring 提取字符一直到字符串末尾。
如果任一参数小于 0 或为 NaN,则被当作 0。 如果任一参数大于 stringName.length,则被当作 stringName.length。 如果 a 大于 b,则 substring 的执行效果就像两个参数调换了一样。见下面的例子。
var anyString = "Mozilla";
// 输出 "Moz"
console.log(anyString.substring(0,3));
console.log(anyString.substring(3,0));
console.log(anyString.substring(3,-3));
console.log(anyString.substring(3,NaN));
console.log(anyString.substring(-2,3));
console.log(anyString.substring(NaN,3));
// 输出 "lla"
console.log(anyString.substring(4,7));
console.log(anyString.substring(7,4));
// 输出 ""
console.log(anyString.substring(4,4));
// 输出 "Mozill"
console.log(anyString.substring(0,6));
// 输出 "Mozilla"
console.log(anyString.substring(0,7));
console.log(anyString.substring(0,10));
# 3、字符串替换
# replace()
替换指定字符串,并返回一个新的字符串,不改变原字符串
string.replace(searchvalue, newvalue)
searchvalue:一个RegExp 对象或者其字面量,要替换的字符串;
newvalue:用于替换掉第一个参数在原字符串中的匹配部分的字符串,该参数可以为一个function函数
let str = "abcdef";
str.replace("c", "z") // 输出结果:abzdef
# 4、字符串转数字
# parseInt()
解析一个字符串并返回指定基数的十进制整数
parseInt(string, radix)
string:字符串,既被解析的值
radix :可选从 2 到 36,表示字符串的基数。例如指定 16 表示被解析值是十六进制数。请注意,10不是默认值!
由于不是所有的浏览器都是默认采用的10进制方案进行的,因此,在使用 parseInt 时,一定要指定一个 radix。
parseInt("50",10); // 输出结果:50
# parseFloat()
函数解析一个参数(必要时先转换为字符串)并返回一个浮点数。
给定值被解析成浮点数。如果给定值不能被转换成数值,则会返回 NaN。
parseFloat("10.01") // 输出结果:10.01
# 数组操作技巧
# 1、求交集
利用filter测试数组中的每一个元素,在使用includes来判断是否有相同元素,如果有相同的元素则将
返回在一个新的数组中
实例:
let a=[1,2,3,4,5,6],b=[4,5,6,7,8,9];
方法1
let intersection = a.filter(v => b.includes(v)) // [4,5,6]
方法2
let aSet = new Set(a)
let bSet = new Set(b)
let intersection = Array.from(new Set(a.filter(v => bSet.has(v))))
# 2、求并集
方法1
let union = a.concat(b.filter(v => !a.includes(v))) // [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
方法2
let aSet = new Set(a)
let bSet = new Set(b)
let union = Array.from(new Set(a.concat(b)))
# 3、求差集
方法1
let difference = a.concat(b).filter(v => !a.includes(v) || !b.includes(v)) // [1,2,3,7,8,9]
方法2
let aSet = new Set(a)
let bSet = new Set(b)
let difference = Array.from(new Set(a.concat(b).filter(v => !aSet.has(v) || !bSet.has(v))))
# 数据类型转换
数据原型
const tree = [
{
name: "一号",
age: 100,
children: [
{
name: "一号大儿子",
age: 75,
children: [
{
name: "一号大孙子",
age: 50,
children: [{ name: "一号大重孙子", age: 25, children: [] }],
},
{ name: "一号二孙子", age: 49, children: [] },
],
},
{
name: "一号二儿子",
age: 65,
children: [
{ name: "一号二儿子的大儿子", age: 38, children: [] },
{ name: "一号二儿子的二儿子", age: 35, children: [] },
],
},
],
},
],
# 1、tree树形转list数组
算法的实现主要分为两种:递归和非递归
# 非递归 (队列方式)
treeConversionListArray(tree) {
const list = [];
const queue = [...tree];
while (queue.length) {
// 方法一:沿着树的宽度遍历节点。采用队列来辅助完成广度遍历。
const node = queue.shift();
// 方法二:沿着树的深度遍历。采用栈来辅助完成深度遍历。
const node = queue.pop();
console.log(node);
const nodeChildren = node.children;
if (nodeChildren) {
queue.push(...nodeChildren);
}
const { children, ...other } = node;
list.push(other);
}
console.log(list);
return list;
},
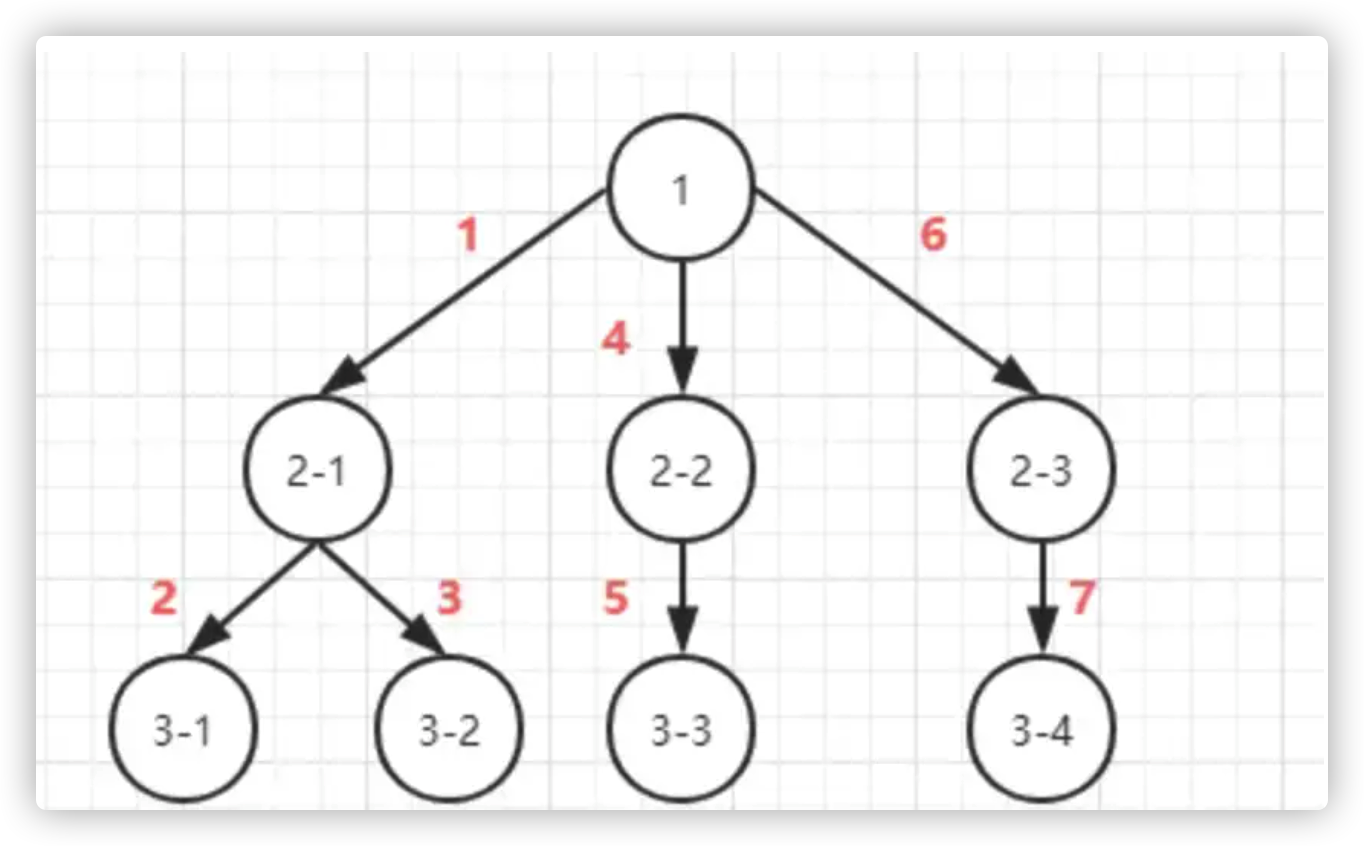
深度优先遍历(DFS):至上而下的遍历
该方法是以纵向的维度对dom树进行遍历,从一个dom节点开始,一直遍历其子节点,直到它的所有子节点都被遍历完毕之后在遍历它的兄弟节点
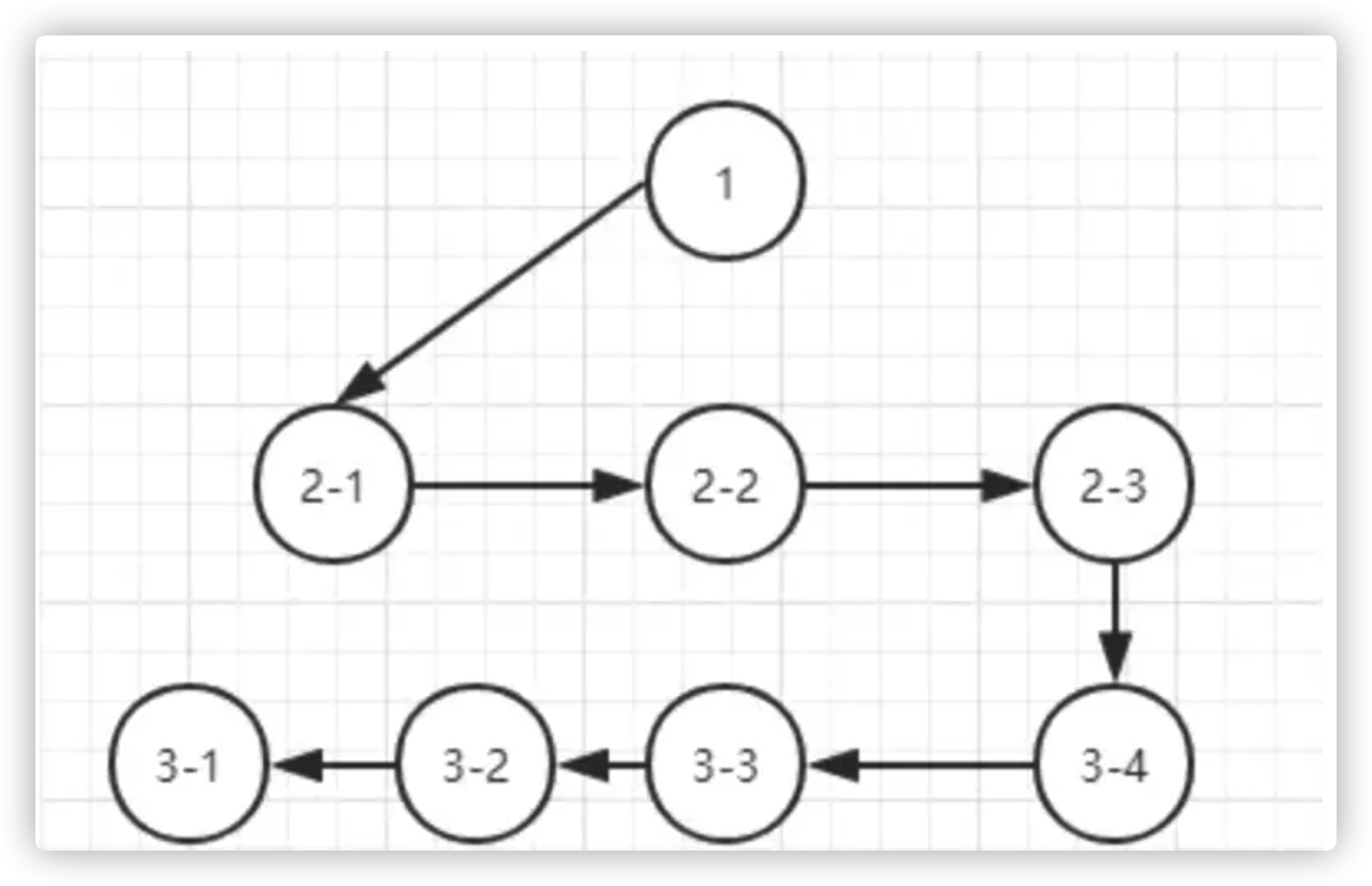
广度优先遍历(BFT):逐层深入的遍历
该方法是以横向的维度对dom树进行遍历,从该节点的第一个子节点开始,遍历其所有的兄弟节点,再遍历第一个节点的子节点,完成该遍历之后,暂时不深入,开始遍历其兄弟节点的子节点。
# 递归方式
treeConversionListArray(tree) {
const dataList = tree.map((i) => {
return deepFirstSearch(i, []);
});
function deepFirstSearch(node, nodeList) {
if (node) {
nodeList.push(node);
const children = node.children;
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++)
// 每次递归的时候将 需要遍历的节点 和 节点所存储的数组传下去
deepFirstSearch(children[i], nodeList);
}
return nodeList;
}
结果
{name: "一号", age: 100},
{name: "一号大儿子", age: 75}
{name: "一号二儿子", age: 65}
{name: "一号二孙子", age: 49}
{name: "一号二儿子的大儿子", age: 38}
{name: "一号二儿子的二儿子", age: 35}
{name: "一号大孙子", age: 50}
{name: "一号大重孙子", age: 25}
# 2、list数组转tree树形
# 方法一:双层循环
listConversionTree(list) {
list.forEach((child) => {
const pid = child.pid;
if (pid) {
list.forEach((parent) => {
if (parent.id === pid) {
parent.children = parent.children || [];
parent.children.push(child);
}
});
}
});
return list.filter((n) => !n.pid);
}
# 方法二:递归组装
listConversionTree(list) {
const tree = [];
for (const node of list) {
// 如果没有pid就可以认为是根节点
if (!node.pid) {
let p = { ...node };
p.children = getChildren(p.id, list);
tree.push(p);
}
}
function getChildren(id, list) {
const children = [];
for (const node of list) {
if (node.pid === id) {
children.push(node);
}
}
for (const node of children) {
const children = getChildren(node.id, list);
if (children.length) {
node.children = children;
}
}
return children;
}
console.log(tree);
return tree;
}